Introduction
A stroke is a serious medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either by a blockage or a ruptured blood vessel. Without prompt intervention, the lack of oxygen and nutrients can lead to permanent brain damage or even death.
Recognizing the early signs of stroke and acting quickly can prevent long-term complications and save lives. At VishwaRaj Hospital, we specialize in advanced stroke care, combining state-of-the-art facilities with compassionate, patient-focused care to ensure the best outcomes for our patients.
Don’t underestimate the importance of awareness—read on to learn everything you need to know about strokes.
Early recognition of stroke symptoms can save lives. Act fast and stay informed.
What is a Stroke?
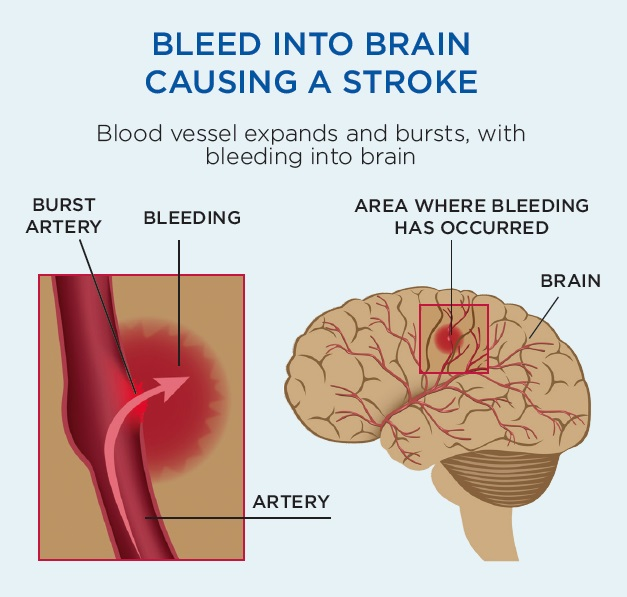
A stroke occurs when the blood flow to the brain is disrupted, depriving brain cells of oxygen and nutrients. The severity of a stroke depends on how quickly medical intervention is provided.
But did you know that not all strokes are the same? Let’s dive deeper into the different types:
Types of Stroke
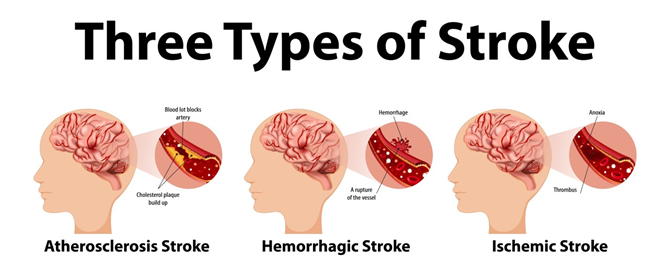
- Ischemic Stroke:
This is the most common type of stroke, caused by a blood clot or plaque blocking an artery that supplies blood to the brain. It accounts for approximately 87% of all strokes and often develops from conditions like atherosclerosis. - Hemorrhagic Stroke:
This occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to bleeding that damages surrounding brain tissue. Hemorrhagic strokes are less common but far more severe, often linked to high blood pressure or aneurysms. - Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA):
Known as a mini stroke, a TIA is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. Although the symptoms resolve within minutes or hours, a TIA serves as a critical warning sign of an impending stroke.
Still wondering how these types differ? Think of a TIA as your brain’s early alarm system—it’s a signal that demands immediate attention.
At VishwaRaj Hospital, we use advanced imaging techniques and diagnostics to accurately identify the type of stroke and administer tailored treatments, ensuring the best chance of recovery.
Key Symptoms of a Stroke
Recognizing the symptoms of a stroke early is critical for timely medical care. The faster you act, the better the outcomes.
Common Symptoms:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- Confusion or trouble speaking and understanding speech.
- Vision problems in one or both eyes.
- Difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of balance.
- Severe headache with no known cause.
These symptoms may appear suddenly and without warning. But that’s not all—there are also lesser-known symptoms to watch for.
Lesser-Known Symptoms:
- Sudden nausea or vomiting.
- Unexplained fatigue or disorientation, especially in younger individuals.
Did you know? Some strokes may present only minor symptoms at first, which makes it even more crucial to seek medical help immediately.
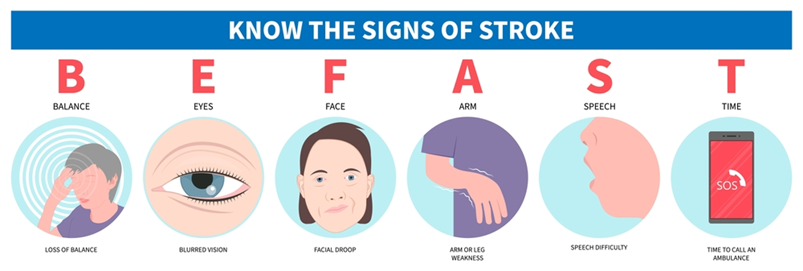
The F.A.S.T. Approach
When it comes to strokes, every second counts. That’s why the F.A.S.T. acronym is a lifesaving tool for identifying and responding to symptoms:
- Face: Is one side of the face drooping? Ask the person to smile and observe any unevenness.
- Arms: Raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- Speech: Is the speech slurred or strange? Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence.
- Time: Time is critical. Call emergency services immediately if you notice any of these signs.
Remember: A stroke can strike without warning, so acting fast can mean the difference between life and death.
We encourage everyone to learn the F.A.S.T. approach. It’s simple, effective, and could save a life.
Learn the F.A.S.T. approach and share it—it’s a simple way to make a big impact in emergencies.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes strokes can help with preventing strokes and minimizing risks.
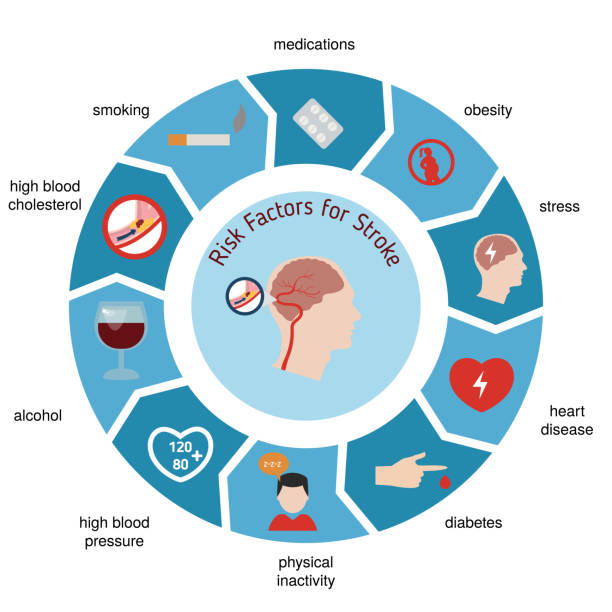
Common Causes:
- High Blood Pressure: This is the leading cause of strokes, making regular monitoring crucial.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of clot formation.
- Obesity: Excess weight strains the heart and vascular system, heightening stroke risk.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels over time.
- Heart Disease: Conditions like atrial fibrillation significantly increase stroke risk.
Underestimated Risk Factors:
- Stress: Prolonged stress not only raises blood pressure but also weakens your overall cardiovascular health.
- Sleep Apnea: Interruptions in breathing during sleep lower oxygen levels, increasing stroke risk over time.
Are you aware of your own risk factors? Taking proactive measures today can safeguard your health tomorrow.
Our specialists work closely with patients to manage these risk factors through personalized care plans, reducing the chances of a stroke or transient ischaemic attack.
How to Prevent a Stroke
Preventing a stroke requires a combination of healthy habits and regular medical check-ups. Here’s how you can take charge:
- Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Levels:
Regular monitoring and appropriate medications are crucial for stroke prevention. - Eat a Balanced Diet:
Focus on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids. - Stay Physically Active:
Exercise not only improves cardiovascular health but also reduces stress, a hidden stroke risk. - Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol:
Both habits significantly increase the risk of strokes and other cardiovascular conditions. - Regular Health Check-Ups:
Early detection of conditions like atrial fibrillation can prevent strokes before they occur.
Taking small steps today can help prevent significant challenges in the future. Are you ready to make the change?
Why Early Detection Matters
Early detection can drastically improve recovery outcomes for stroke patients. Treatments such as thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy are time-sensitive and most effective when administered within hours of the first signs of a stroke.
We are equipped with advanced technologies and a dedicated stroke care team to ensure prompt intervention, reducing the risk of severe complications.
Recognize the signs of a stroke and ensure timely intervention—it can save lives.