What happens if you have Glaucoma?
- Written by: Department Of Ophthalmology
- Published: March 31, 2021
- 4 min Read

Glaucoma is a defect in the eyes where your optic nerve suffers through damage. The primary purpose of the optic nerve is to carry information from your eyes to the brain. You usually suffer from Glaucoma as a result of high pressure in your eyes. The continuing pressure on the eye erodes the optic nerve leading to Glaucoma or sometimes blindness. At the early stages of Glaucoma, it is easy to treat it.
Symptoms that you will experience
The nature of the symptom that you will experience will depend on the type of Glaucoma you are suffering through:
- Open-Angle Glaucoma
This eye condition has several names; it is also famous as primary open-angle Glaucoma and chronic open-angle Glaucoma. Moreover, it is the most common type of glaucoma disease. Typically there are no warning symptoms or signs of the disease. It develops slowly and gradually, with time without any noticeable vision problem.
Additionally, most people do not experience any change in vision because, initially, there is peripheral vision loss. The sharpness in your eyesight remains intact until late for the treatment. So to detect the problem early, you should go for a regular eye check-up.
- Acute closed Glaucoma
Acute closed Glaucoma, also known as narrow-angle Glaucoma, has the worst eye-pain. The angle is closed or narrowed from most of the part, increasing the pressure in the eye. This rise may cause a sudden and acute attack. However, in the early stages of the disease, the angle may be narrow but does not pressurize the eyes. Thus your optic nerve remains unaffected. Signs of acute closed Glaucoma are very noticeable and sudden. The following are the symptoms:
- Headaches
- Halos surrounding light
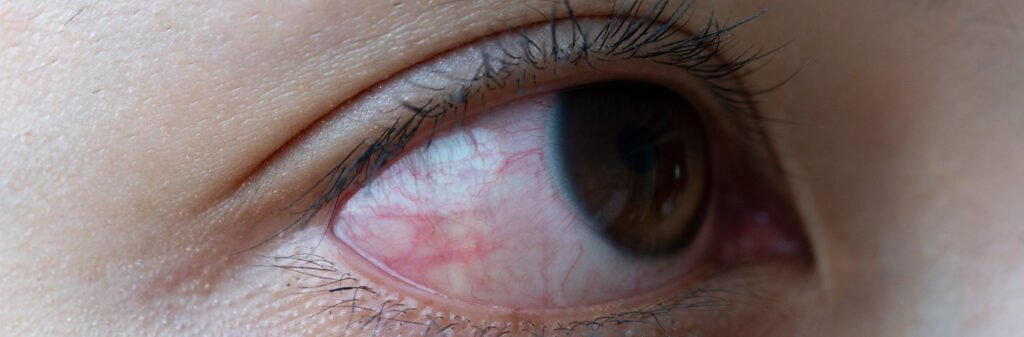
- Red-eye
- Dilated pupils
- Blurry vision
- Vomiting and nausea
- Severe pain in the eye.
Thus if you experience this type of Glaucoma, you should consult a doctor immediately. The defect will start damaging the optic nerve in a few hours only. Moreover, if you do not treat it within 6 to 12 hours, it may lead to complete permanent blindness. It can also result in a permanently enlarged pupil.
- Congenital Glaucoma in Babies
It is usually common in newborn babies or of a few years. Symptoms of the disease are:
- Your baby has increased sensitivity to light and contraction.
- The cornea is becoming bigger. Also, your baby’s cornea gets transparently clouded.
- Frequent rubbing of eyes, blinking or shutting eyes all the time.
Secondary Glaucoma and other problems
You experience symptoms depending on what is the cause behind increasing pressure on your eyes. Thus, if you experience inflammation in the eyes, you will see halos around light. Additionally, you will have difficulty keeping your eyes open in bright light, also known as photophobia.
Conclusion
Other eye injuries like retinal detachment, edema, and bleeding can hide the signs or symptoms of Glaucoma. If you are suffering from a cataract, the condition of your vision will get worse. So by getting it checked with your doctor can confirm if you have Glaucoma or not.
Related Read
Retinitis pigmentosa and its effect on the quality of life
Retinitis pigmentosa and its effect on the quality of life: